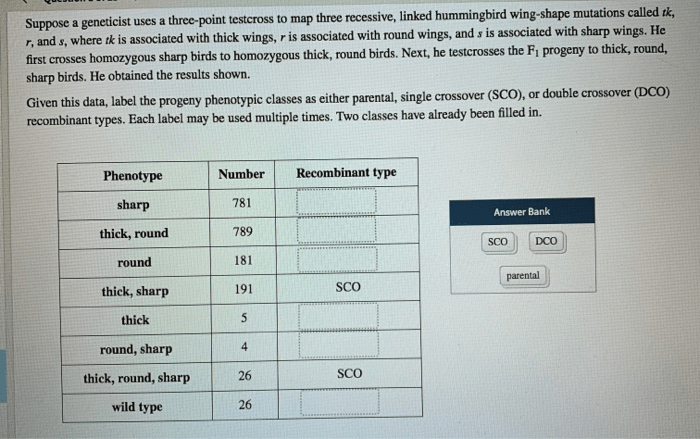
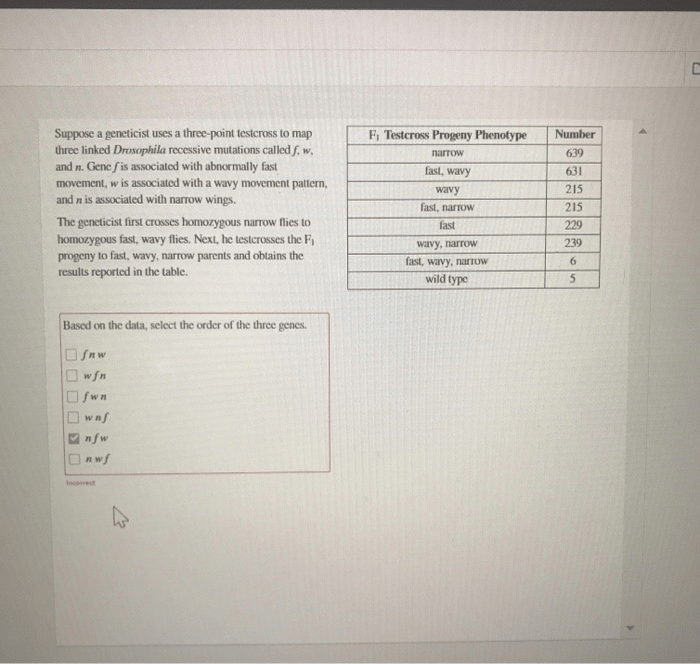
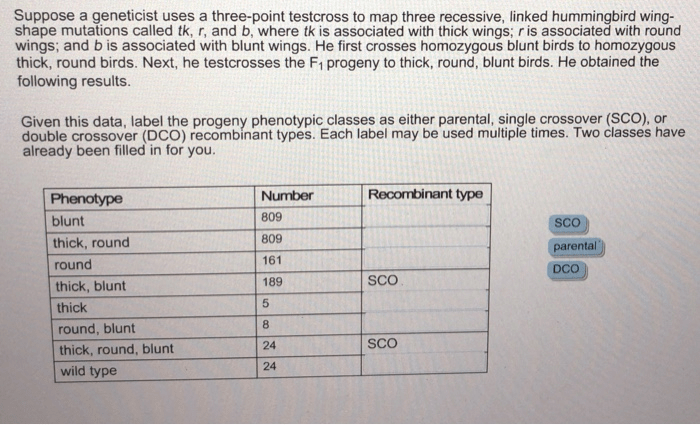
Suppose a geneticist uses a three-point testcross: what insights can be gained? This genetic technique offers a powerful tool to unravel the mysteries of genetic inheritance, revealing the intricate relationships between genes and their impact on traits. By embarking on a three-point testcross, geneticists can map genes, study genetic disorders, and uncover the secrets of genetic inheritance.
Three-point testcrosses involve crossing a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual at three different gene loci. This allows for the calculation of recombination frequencies between the three genes, providing valuable information about their genetic linkage. The analysis of testcross data enables geneticists to identify and interpret genetic linkage, providing insights into the physical arrangement of genes on chromosomes.
Introduction: Suppose A Geneticist Uses A Three-point Testcross
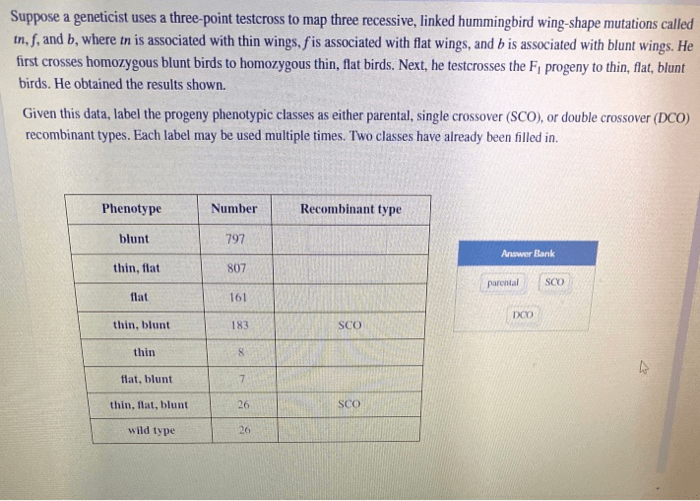
A three-point testcross is a genetic analysis technique used to determine the linkage relationships between three genes. It involves crossing a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual and analyzing the resulting progeny to determine the recombination frequencies between the genes.
Three-point testcrosses are useful for mapping genes, studying genetic disorders, and understanding the genetic architecture of complex traits.
Procedure, Suppose a geneticist uses a three-point testcross
The steps involved in performing a three-point testcross are as follows:
- Cross a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual.
- Analyze the resulting progeny to determine the recombination frequencies between the three genes.
Data Analysis
The data from a three-point testcross can be analyzed using a variety of statistical methods. The most common method is to use a chi-square test to determine whether the observed recombination frequencies are significantly different from the expected recombination frequencies.
If the observed recombination frequencies are significantly different from the expected recombination frequencies, then this indicates that the genes are linked.
Applications
Three-point testcrosses have a wide range of applications in genetics, including:
- Mapping genes
- Studying genetic disorders
- Understanding the genetic architecture of complex traits
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of a three-point testcross?
A three-point testcross aims to determine the recombination frequencies between three genes and identify genetic linkage, providing insights into the physical arrangement of genes on chromosomes.
How is a three-point testcross performed?
A three-point testcross involves crossing a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual at three different gene loci, allowing for the calculation of recombination frequencies.
What information can be obtained from a three-point testcross?
Three-point testcrosses provide information about recombination frequencies and genetic linkage, enabling geneticists to map genes, study genetic disorders, and understand the genetic basis of traits.