Embark on an in-depth exploration of solutions electrolytes and concentration lab 14, delving into the fundamental concepts, applications, and practical implications of these essential components in various fields.
Solutions, electrolytes, and concentration play a pivotal role in numerous scientific disciplines and everyday life. This introduction provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, laying the groundwork for a deeper understanding of their significance.
Electrolyte Solutions: Solutions Electrolytes And Concentration Lab 14
Electrolyte solutions are mixtures that contain ions, which are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained electrons. These ions are able to conduct electricity, which is why electrolyte solutions are often used in batteries and other electrical devices.
There are two main types of electrolytes: strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes. Strong electrolytes completely dissociate into ions when they are dissolved in water, while weak electrolytes only partially dissociate. Some examples of strong electrolytes include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Some examples of weak electrolytes include acetic acid (CH3COOH) and ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
Concentration of Electrolyte Solutions
The concentration of an electrolyte solution is a measure of the amount of solute (the ions) that is dissolved in a given amount of solvent (the water). The concentration of an electrolyte solution can be expressed in several different units, including molarity (M), molality (m), and parts per million (ppm).
The concentration of an electrolyte solution can affect its conductivity. The higher the concentration of an electrolyte solution, the more ions are present, and the more easily the solution can conduct electricity.
Lab 14: Solutions, Electrolytes, and Concentration, Solutions electrolytes and concentration lab 14
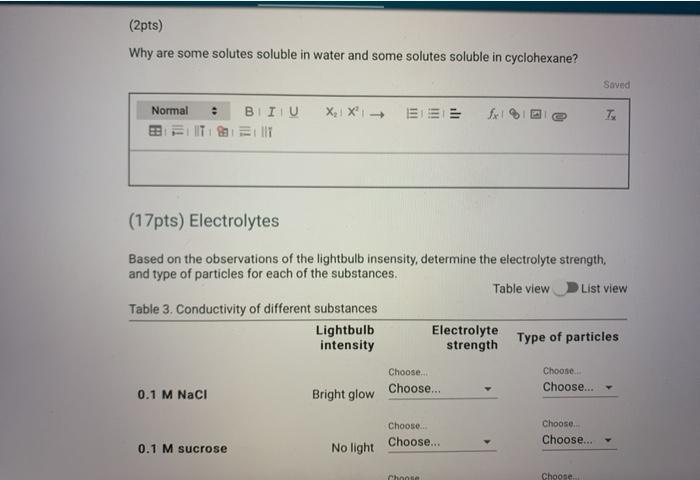
Lab 14 is a laboratory experiment that investigates the properties of electrolyte solutions. In this lab, students will learn how to prepare electrolyte solutions, measure the concentration of electrolyte solutions, and test the conductivity of electrolyte solutions.
The expected results of Lab 14 are that students will be able to:
- Prepare electrolyte solutions of different concentrations.
- Measure the concentration of electrolyte solutions using a conductivity meter.
- Test the conductivity of electrolyte solutions and relate the conductivity to the concentration of the solution.
Applications of Electrolyte Solutions
Electrolyte solutions have a wide variety of applications in everyday life. Some of the most common applications include:
- Batteries: Electrolyte solutions are used in batteries to conduct electricity between the positive and negative terminals.
- Electroplating: Electrolyte solutions are used in electroplating to deposit a thin layer of metal on a surface.
- Water purification: Electrolyte solutions are used in water purification to remove impurities from water.
- Medicine: Electrolyte solutions are used in medicine to treat dehydration and other electrolyte imbalances.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of Lab 14?
Lab 14 aims to provide students with hands-on experience in understanding the concepts of electrolyte solutions and concentration.
What are the different types of electrolytes?
Electrolytes can be classified into strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and non-electrolytes based on their ability to dissociate into ions in solution.
How is the concentration of electrolyte solutions measured?
The concentration of electrolyte solutions can be expressed in various units, including molarity, molality, and normality.