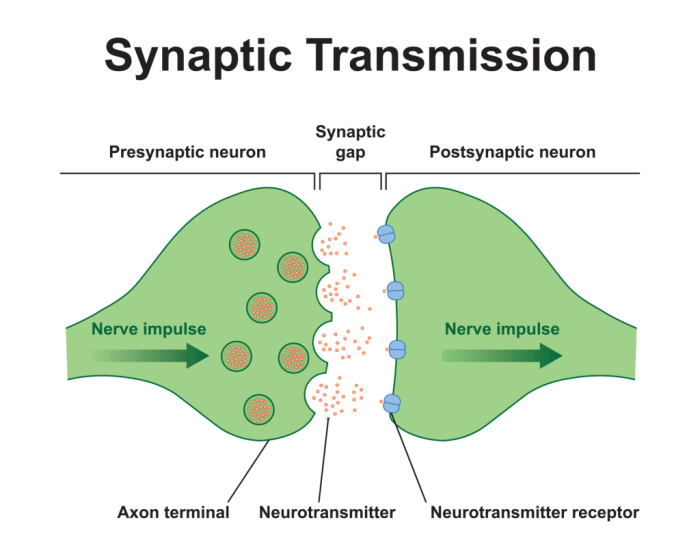
Match each neural component with its role in synaptic transmission. This exploration delves into the intricate mechanisms of neural communication, shedding light on the fundamental processes that govern the brain’s remarkable functions.
Synaptic transmission, the cornerstone of neuronal communication, involves a symphony of specialized components, each playing a distinct role in the seamless relay of information. Understanding these components and their functions is paramount to unraveling the complexities of the nervous system.
1. Neural Components Involved in Synaptic Transmission
Synaptic transmission is the process by which neurons communicate with each other. It involves the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron, their diffusion across the synaptic cleft, and their binding to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. The following table summarizes the neural components involved in synaptic transmission:
| Neural Component | Structure | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Presynaptic neuron | Axon terminal | End of the axon | Releases neurotransmitters |
| Postsynaptic neuron | Dendrite | Extension of the cell body | Receives neurotransmitters |
| Synaptic cleft | Gap between neurons | Separates presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons | Allows neurotransmitters to diffuse |
| Neurotransmitter | Chemical messenger | Released from presynaptic neuron | Binds to receptors on postsynaptic neuron |
| Receptors | Proteins | Embedded in postsynaptic neuron membrane | Bind to neurotransmitters and trigger responses |
2. Role of Presynaptic Neuron
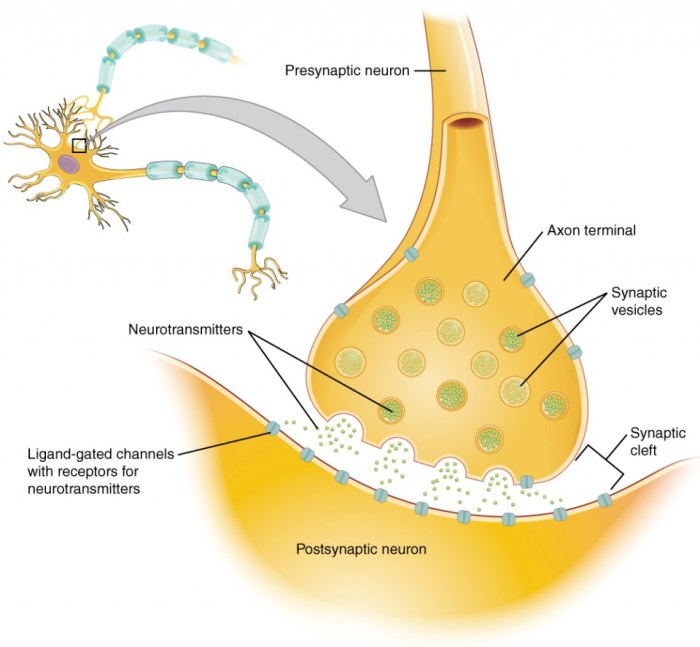
The presynaptic neuron is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. This process involves the following steps:1.
-
-*Neurotransmitter synthesis
Neurotransmitters are synthesized in the cell body of the presynaptic neuron.
- 2.
- 3.
-*Neurotransmitter storage
Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles within the axon terminal.
-*Neurotransmitter release
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft.
The diagram below illustrates the presynaptic neuron and its components:[Diagram of presynaptic neuron]
3. Role of Postsynaptic Neuron: Match Each Neural Component With Its Role In Synaptic Transmission.
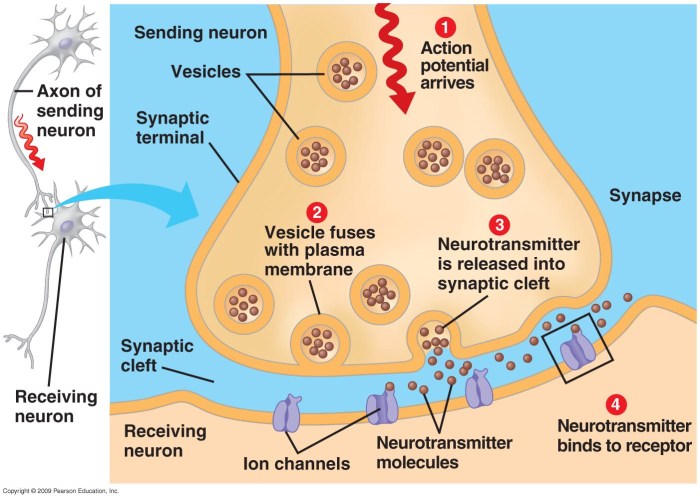
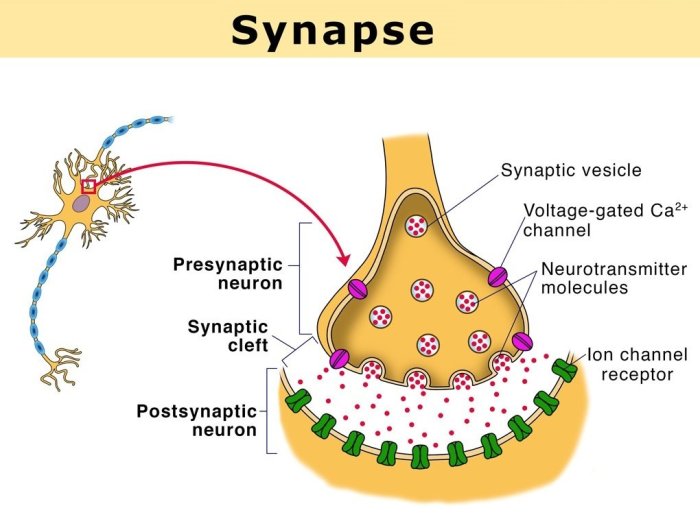
The postsynaptic neuron is responsible for receiving and responding to neurotransmitters. This process involves the following steps:1.
-
-*Neurotransmitter binding
Neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
- 2.
- 3.
-*Signal transduction
The binding of neurotransmitters to receptors triggers a cascade of events that ultimately leads to a change in the electrical activity of the postsynaptic neuron.
-*Cellular response
The change in electrical activity of the postsynaptic neuron can lead to a variety of cellular responses, such as the opening of ion channels, the synthesis of proteins, or the activation of other signaling pathways.
The diagram below illustrates the postsynaptic neuron and its components:[Diagram of postsynaptic neuron]
Questions Often Asked
What is the role of the presynaptic neuron in synaptic transmission?
The presynaptic neuron is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, initiating the transmission of signals across the synapse.
How do neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic neuron?
Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, triggering a cascade of events that can either excite or inhibit the neuron’s activity.
What is the function of the synaptic cleft?
The synaptic cleft is the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons, across which neurotransmitters diffuse to facilitate communication.