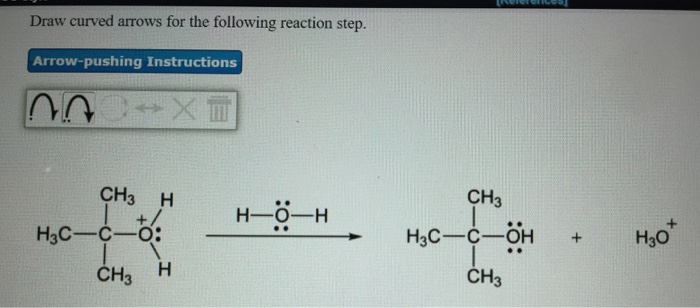
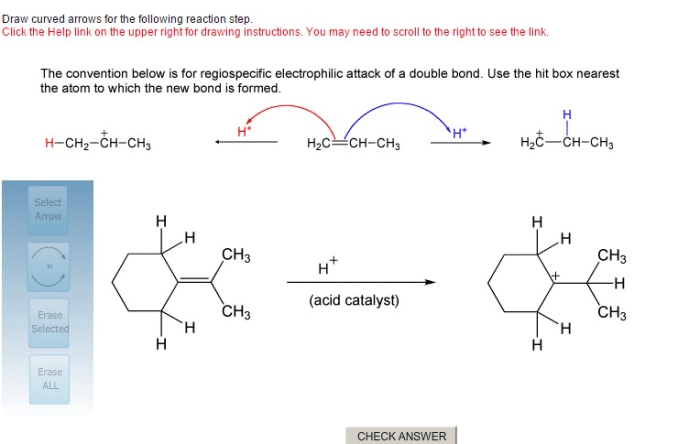
Draw curved arrows for the following reaction step. – In organic chemistry, drawing curved arrows is an essential skill for understanding and analyzing reaction mechanisms. Curved arrows represent the flow of electrons during a chemical reaction, providing valuable insights into the reaction pathway and the formation of products. This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of drawing curved arrows, exploring the rules, conventions, and applications of this powerful tool.
Drawing curved arrows involves following specific guidelines to accurately depict the movement of electrons. By understanding the principles behind curved arrow notation, chemists can gain a deeper comprehension of organic reactions and design synthetic strategies more effectively.
Introduction
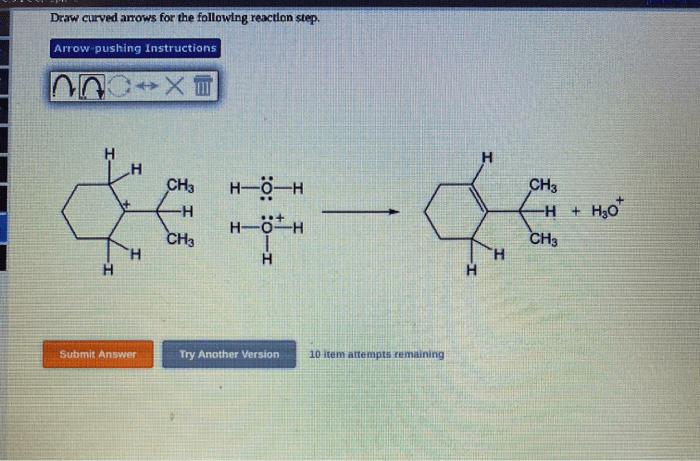
Curved arrows are a fundamental tool in organic chemistry. They represent the flow of electrons in a reaction and are essential for understanding reaction mechanisms. Curved arrows can be used to depict a variety of reactions, including nucleophilic attack, electrophilic addition, and radical reactions.
Drawing Curved Arrows: Draw Curved Arrows For The Following Reaction Step.
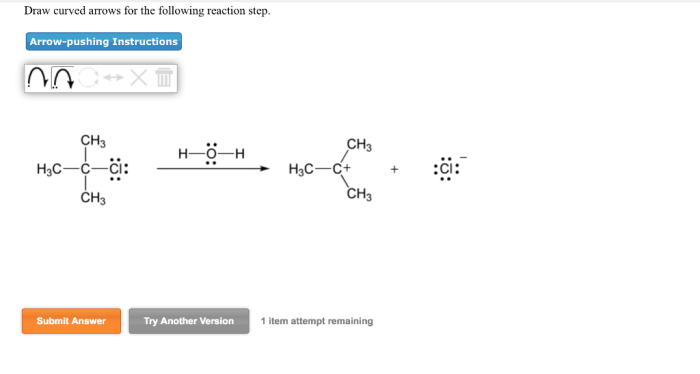
The basic rules for drawing curved arrows are as follows:
- The arrowhead points to the atom or group of atoms that is gaining electrons.
- The tail of the arrow points to the atom or group of atoms that is losing electrons.
- The arrow should be drawn so that it follows the path of the electrons.
Examples and Applications, Draw curved arrows for the following reaction step.
Here are some examples of how curved arrows can be used to depict different types of reactions:
- Nucleophilic attack:In a nucleophilic attack, a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) attacks an electrophile (an electron-poor species). The curved arrow shows the movement of electrons from the nucleophile to the electrophile.
- Electrophilic addition:In an electrophilic addition, an electrophile adds to a double bond. The curved arrow shows the movement of electrons from the double bond to the electrophile.
- Radical reactions:In a radical reaction, a radical (a species with an unpaired electron) reacts with another species. The curved arrow shows the movement of the unpaired electron.
Advanced Topics
Curved arrows can also be used to depict more complex reaction mechanisms, such as pericyclic reactions and radical reactions. In addition, curved arrows can be used in computational chemistry and reaction modeling.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of drawing curved arrows in organic chemistry?
Curved arrows are used to represent the movement of electrons during a chemical reaction, providing a visual representation of the reaction mechanism.
What are the rules for drawing curved arrows?
Curved arrows must start from a region of high electron density and end at a region of low electron density. They should not cross each other or violate any chemical bonding rules.
How can curved arrows be used to analyze reaction mechanisms?
By following the flow of electrons indicated by curved arrows, chemists can determine the sequence of bond breaking and bond formation events that occur during a reaction.